CI for difference between two population proportions
In this tutorial we will discuss some examples on confidence interval for difference between two population proportions.
Example 1
A random sample of 85 parts manufactured by machine A yields 10 defective and a random sample of 110 parts manufactured by machine B shows 28 defective.
Compute 95% confidence interval for difference between the proportions of defectives.
Are the two machine differ significantly with respect to the proportion of defectives?
Solution
Given information
| . | Machine A | Machine B |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size | $n_1=85$ | $n_2=110$ |
| Observed no. of defectives | $X_1=10$ | $X_2=28$ |
We wish to determine $95$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$.
Step 1 Specify the confidence level
Confidence level is $1-\alpha = 0.95$. Thus, the level of significance is $\alpha = 0.05$.
Step 2 Given information
Given that $X_1 = 10$, $X_2 = 28$, $n_1 = 85$, $n_2 = 110$.
The estimate of the population proportions $p_1$ is $\hat{p}_1 =\frac{X_1}{n_1} =\frac{10}{85}=0.1176$ and the estimate of the population proportion $p_2$ is $\hat{p}_2 =\frac{X_2}{n_2} =\frac{28}{110}=0.2545$.
Step 3 Specify the formula
$100(1-\alpha)$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) - E \leq (p_1 -p_2) \leq (\hat{p}_1 -\hat{p}_2)+ E. \end{aligned} $$
where $E = Z_{\alpha/2} \sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}_1*(1-\hat{p}_1)}{n_1}+\frac{\hat{p}_2*(1-\hat{p}_2)}{n_2}}$ and $Z_{\alpha/2}$ is the $Z$ value providing an area of $\alpha/2$ in the upper tail of the standard normal probability distribution.
Step 4 Determine the critical value
The critical value of $Z$ for given level of significance is $Z_{\alpha/2}$.
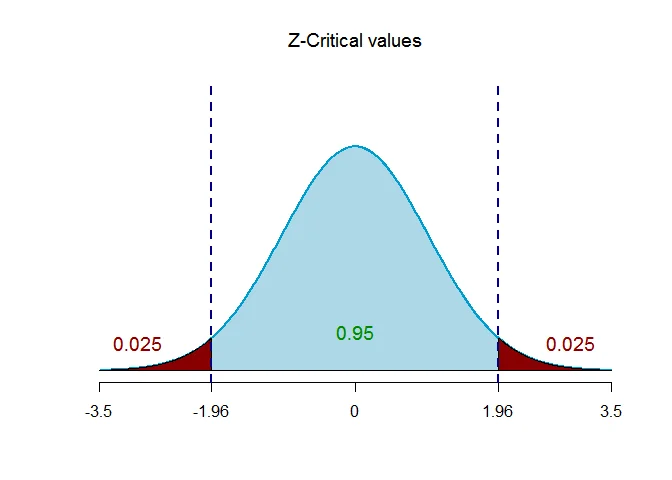
Thus $Z_{\alpha/2} = Z_{0.025} = 1.96$.
Step 5 Compute the margin of error
The margin of error for the difference $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} E & = Z_{\alpha/2} \sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}_1*(1-\hat{p}_1)}{n_1}+\frac{\hat{p}_2*(1-\hat{p}_2)}{n_2}}\\ & = 1.96 \sqrt{\frac{0.1176*(1-0.1176)}{85}+\frac{0.2545*(1-0.2545)}{110}}\\ &= 0.1064. \end{aligned} $$
Step 6 Determine the confidence interval
$95$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) - E &\leq (p_1-p_2) \leq (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) + E\\ (0.1176-0.2545) - 0.1064 & \leq (p_1-p_2) \leq (0.1176-0.2545) + 0.1064\\ -0.2433 & \leq (p_1-p_2) \leq -0.0305 \end{aligned} $$
Thus, $95$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is $(-0.2433,-0.0305)$.
Interpretation
We can be $95$% confident that the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is between $-0.2433$ and $-0.0305$.
Because the $95$% confidence interval does not include the point zero, we conclude that at $0.05$ level of significance the two machine differ significantly with respect to the proportion of defectives.
Example 2
In a recent survey of randomly selected adults 65 or older, 411 of 1012 men and 525 of 1062 women say they suffer from some form of arthritis.
a. Construct a 98% confidence interval for the difference between senior men and women who suffer from arthritis.
b. Does there appear to be a difference between senior men and women as far as suffering from arthritis?
Solution
Given information
| . | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size | $n_1=1012$ | $n_2=1062$ |
| Suffering from arthritis | $X_1=411$ | $X_2=525$ |
We want to determine $98$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$.
Step 1 Specify the confidence level
Confidence level is $1-\alpha = 0.98$. Thus, the level of significance is $\alpha = 0.02$.
Step 2 Given information
Given that $X_1 = 411$, $X_2 = 525$, $n_1 = 1012$, $n_2 = 1062$.
The estimate of the population proportions $p_1$ is $\hat{p}_1 =\frac{X_1}{n_1} =\frac{411}{1012}=0.4061$ and the estimate of the population proportion $p_2$ is $\hat{p}_2 =\frac{X_2}{n_2} =\frac{525}{1062}=0.4944$.
Step 3 Specify the formula
$100(1-\alpha)$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) - E \leq (p_1 -p_2) \leq (\hat{p}_1 -\hat{p}_2)+ E. \end{aligned} $$
where $E = Z_{\alpha/2} \sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}_1*(1-\hat{p}_1)}{n_1}+\frac{\hat{p}_2*(1-\hat{p}_2)}{n_2}}$ and $Z_{\alpha/2}$ is the $Z$ value providing an area of $\alpha/2$ in the upper tail of the standard normal probability distribution.
Step 4 Determine the critical value
The critical value of $Z$ for given level of significance is $Z_{\alpha/2}$.

Thus $Z_{\alpha/2} = Z_{0.01} = 2.33$.
Step 5 Compute the margin of error
The margin of error for the difference $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} E & = Z_{\alpha/2} \sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}_1*(1-\hat{p}_1)}{n_1}+\frac{\hat{p}_2*(1-\hat{p}_2)}{n_2}}\\ & = 2.33 \sqrt{\frac{0.4061*(1-0.4061)}{1012}+\frac{0.4944*(1-0.4944)}{1062}}\\ &= 0.0507. \end{aligned} $$
Step 6 Determine the confidence interval
$98$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) - E &\leq (p_1-p_2) \leq (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) + E\\ (0.4061-0.4944) - 0.0507 & \leq (p_1-p_2) \leq (0.4061-0.4944) + 0.0507\\ -0.1389 & \leq (p_1-p_2) \leq -0.0375 \end{aligned} $$
Thus, $98$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is $(-0.1389,-0.0375)$.
Interpretation
We can be $98$% confident that the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is between $-0.1389$ and $-0.0375$.
Because the $98$% confidence interval does not include the point zero, we conclude that at $0.02$ level of significance there appears to be significant difference between the proportion of senior men and proportion of women who suffer from arthritis.
Example 3
Two machines used in the same operation are to be compared. A random sample of 80 parts from the first machine yields 6 non-conforming ones. A random sample of 120 parts from the second machine shows 14 non-conforming ones.
Find a 95% confidence interval for difference in the proportion of non-conforming parts between the two machines.
Solution
Given information
| . | First Machine | Second Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size | $n_1=80$ | $n_2=200$ |
| no.of non-confirming | $X_1=6$ | $X_2=14$ |
We want to determine $95$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$.
Step 1 Specify the confidence level
Confidence level is $1-\alpha = 0.95$. Thus, the level of significance is $\alpha = 0.05$.
Step 2 Given information
Given that $X_1 = 6$, $X_2 = 14$, $n_1 = 80$, $n_2 = 200$.
The estimate of the population proportions $p_1$ is $\hat{p}_1 =\frac{X_1}{n_1} =\frac{6}{80}=0.075$ and the estimate of the population proportion $p_2$ is $\hat{p}_2 =\frac{X_2}{n_2} =\frac{14}{200}=0.07$.
Step 3 Specify the formula
$100(1-\alpha)$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) - E \leq (p_1 -p_2) \leq (\hat{p}_1 -\hat{p}_2)+ E. \end{aligned} $$
where $E = Z_{\alpha/2} \sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}_1*(1-\hat{p}_1)}{n_1}+\frac{\hat{p}_2*(1-\hat{p}_2)}{n_2}}$ and $Z_{\alpha/2}$ is the $Z$ value providing an area of $\alpha/2$ in the upper tail of the standard normal probability distribution.
Step 4 Determine the critical value
The critical value of $Z$ for given level of significance is $Z_{\alpha/2}$.
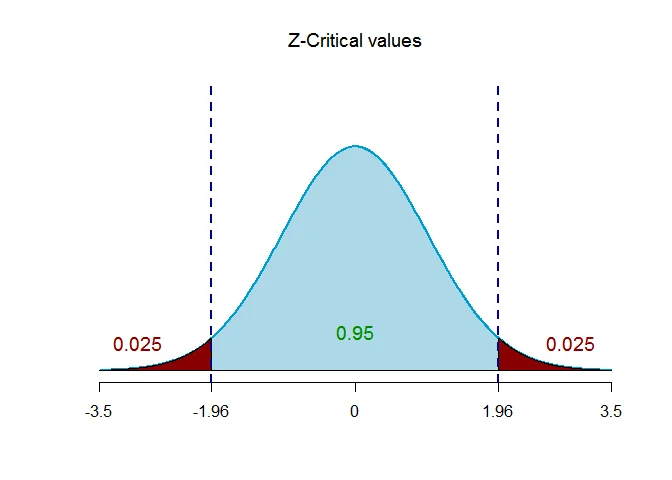
Thus $Z_{\alpha/2} = Z_{0.025} = 1.96$.
Step 5 Compute the margin of error
The margin of error for the difference $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} E & = Z_{\alpha/2} \sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}_1*(1-\hat{p}_1)}{n_1}+\frac{\hat{p}_2*(1-\hat{p}_2)}{n_2}}\\ & = 1.96 \sqrt{\frac{0.075*(1-0.075)}{80}+\frac{0.07*(1-0.07)}{200}}\\ &= 0.0677. \end{aligned} $$
Step 6 Determine the confidence interval
$95$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) - E &\leq (p_1-p_2) \leq (\hat{p}_1-\hat{p}_2) + E\\ (0.075-0.07) - 0.0677 & \leq (p_1-p_2) \leq (0.075-0.07) + 0.0677\\ -0.0627 & \leq (p_1-p_2) \leq 0.0727 \end{aligned} $$
Thus, $95$% confidence interval estimate of the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is $(-0.0627,0.0727)$.
Interpretation
We can be $95$% confident that the difference between two population proportions $(p_1-p_2)$ is between $-0.0627$ and $0.0727$.
Because the $95$% confidence interval include the point zero, we conclude that at $0.05$ level of significance there is no significant difference between the proportion of non-confirming parts between the two machines.